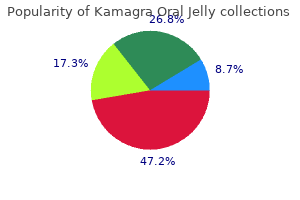
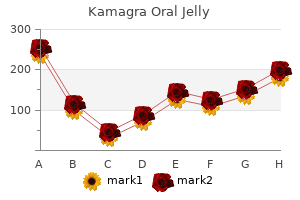
|
"Kamagra oral jelly 100 mg buy with visa, erectile dysfunction doctors staten island". P. Jarock, M.B.A., M.D. Program Director, Morehouse School of Medicine
Various factors affecting pharmacodynamic drug conduct could embrace age, drug tolerance, drug interactions, and unknown pathophysiologic factors. The use of in vitro biomarkers and in vitro binding studies has been proposed to set up bioequivalence. Study Considerations the basic design for a bioequivalence study is decided by (1) the scientific questions and objectives to be answered, (2) the nature of the reference materials and the dosage kind to be tested, (3) the availability of analytical methods, (4) the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drug substance, (5) the route of drug administration, and (6) benefit�risk and ethical considerations with regard to testing in humans. Pharmacokinetic parameters, pharmacodynamic parameters, scientific observations, and/or in vitro studies could additionally be used to determine drug bioavailability from a drug product. The design and analysis of well-controlled bioequivalence studies require cooperative input from pharmacokineticists, statisticians, clinicians, bioanalytical chemists, and others. However, even with the supply of such tips, the principal investigator should put together an in depth protocol for the research. Some of the elements of a protocol for an in vivo bioavailability examine are listed in Table 16-5. For bioequivalence studies, the take a look at and reference drug formulations should comprise the same drug in the same dose strength and in similar dosage forms (eg, immediate launch or controlled release), and have to be given by the same route of administration. The number of topics in the examine will depend on the anticipated intersubject and intrasubject variability. Patient choice is made in accordance with certain established standards for inclusion in, or exclusion from, the examine. Such variations could end result if generic drugs were compared to totally different reference listed medicine. The reference drug product should be administered by the identical route as the comparison formulations unless an alternative route or further route is required to answer particular pharmacokinetic questions. For instance, if an lively drug is poorly bioavailable after oral administration, the drug could additionally be in comparison with an oral resolution or an intravenous injection. Before beginning an in vivo bioequivalence research, the total content material of the energetic drug substance in the take a look at product (generally the generic product) should be inside 5% of that of the reference product. Moreover, in vitro comparative dissolution or drug-release studies under varied specified situations are usually performed for both test and reference products before performing the in vivo bioequivalence research. The subjects usually quick for 10�12 hours (overnight) prior to drug administration and should proceed to quick for a 2- to 4-hour interval after dosing. Drug exposure parameters should be log-transformed before statistical comparisons. Further element concerning the statistical exams might be provided later in the discussion on bioequivalence examine designs. Frequently Asked Questions �� What are the study protocol concerns for conducting a bioequivalence examine Some of those components are listed below with implications for formulation growth and optimization of dosing regimens. Formulations may be designed to improve the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs, lengthen the absorption phase by slowing the rate of release of medication (controlled-release formulations), or prevent dissolution within the gastric lumen for drugs that are destroyed by gastric acidity (enteric-coated formulations) (see also Chapter 15). An instance of how formulation design can enhance bioavailability is shown by evaluating the immunosuppressant drug cyclosporine systemic exposures offered by the Neoral microemulsion formulation to those supplied by the Sandimmune formulation. Propranolol is almost completely absorbed after oral administration, but because of intensive first-pass metabolism within the liver, solely about 25% of the parent drug reaches the systemic circulation. Prodrugs that endure rapid presystemic metabolism can be utilized to enhance bioavailability, as illustrated by valacyclovir, a prodrug of the nucleoside analog antiviral compound acyclovir. Food can affect bioavailability in numerous ways, similar to affecting gastrointestinal pH, gastric emptying, intestinal transit, splanchnic blood circulate, and first-pass metabolism. If the food effects on drug bioavailability are clinically important, then the drug product labeling will present directions about the means to achieve the optimum dosing regimen-either to take the drug only on an empty abdomen, or only with meals, relying on the character of the bioavailability impact and scientific consequences. As meals prolongs gastric emptying, this increases the length of time that the acid-labile didanosine will keep up a correspondence with a low pH environment. Food-induced increases in drug bioavailability could be either fascinating or undesirable. The food effect on isotretinoin (indicated to treat severe recalcitrant nodular acne) bioavailability is used to optimize the dosing routine. Consequently, the label recommends that isotretinoin capsules ought to always be taken with meals. By contrast, in some circumstances, food-induced increases in oral bioavailability may be related to safety issues. Due to concern that publicity to larger efavirenz systemic bioavailability could result in increased severe antagonistic events, the Sustiva label recommends that efavirenz capsules and tablets be taken on an empty stomach, ideally at bedtime. Changes in drug bioavailability because of drug�drug interactions can happen by way of a variety of mechanisms, similar to inhibition of metabolizing enzymes, induction of metabolizing enzymes, inhibitor of transporters, and induction of transporters. Two examples of drug� drug interactions, certainly one of enzyme inhibition and the second of enzyme induction, will present how the ability of coadministered medication to alter systemic bioavailability impacts both recommendations for optimal dosing regimens and development of new formulations to maximize bioavailability. For drugs similar to sedative hypnotics, antiarrhythmic, and ergot alkaloid preparations, massive increases in systemic bioavailability brought on by ritonavir coadministration can lead to potentially critical and/or life-threatening adverse occasions; thus, ritonavir coadministration with these medication is contraindicated. Enzyme inducers coadministered with drugs can probably lower systemic bioavailability to subtherapeutic levels. An instance is the antibacterial drug rifampin (used in remedy of tuberculosis), Drug Product Performance, In Vivo: Bioavailability and Bioequivalence 489 which is a potent inducer of cytochrome P-450 enzymes. Coadministration of rifampin with medication metabolized by metabolic pathways induced by rifampin may end up in lower bioavailability as a result of acceleration of metabolism. The Rifadin label states that, to preserve optimum therapeutic bioavailability, dosages of medication metabolized by these enzymes could require dose adjustment when starting or stopping concomitantly administered rifampin. Some examples of these medication for which rifampin lowers systemic bioavailability to the extent that dose adjustment is required embrace anticonvulsants, antiarrhythmics, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, fluoroquinolones, oral hypoglycemic brokers, transplant medicine, and tricyclic antidepressants. For some medication, corresponding to oral contraceptives, coadministration with rifampin is contraindicated because of concerns that rifampin coadministration can decrease oral contraceptive systemic bioavailability to subtherapeutic ranges. The cardiac glycoside digoxin is a substrate for P-glycoprotein, on the degree of intestinal absorption, renal tubular secretion, and biliary-intestinal secretion (Hughes and Crowe, 2010). Therefore, medicine that induce or inhibit P-glycoprotein have the potential to alter digoxin bioavailability. As digoxin is a slender therapeutic index drug, small modifications in bioavailability can probably end in critical antagonistic occasions as a result of lack of efficacy (bioavailability is decrease than the therapeutic range) or life-threatening toxicity (bioavailability exceeds the therapeutic range). Impairments within the practical reserve of multiple organs can occur with advancing age, and such impairments may have an effect on drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Advancing age is associated with adjustments similar to decreases in liver mass and perfusion, adjustments in physique composition, and reduces in renal function. As a end result, it is recommended that clinicians carefully monitor dosing regimens and drug action in geriatric sufferers. The bioavailability of medication eliminated primarily through renal excretory mechanisms is likely to enhance in patients with impaired renal operate (Chapter 24). The outcomes of pharmacokinetic studies in hepatic-impaired sufferers may be helpful in determining whether or not dose changes are required in such patients to achieve the same systemic drug bioavailability as in sufferers with normal liver operate. The systemic bioavailability of a drug in patients can differ from that in wholesome regular topics. Ordinarily, sponsors conduct single- and multipledose pharmacokinetic research in both wholesome normal subjects and the goal patient population in early stage growth, to characterize similarities and variations in drug systemic bioavailability. The actual focus of the active drug ingredient or therapeutic moiety, or its active metabolite(s), should be measured with appropriate precision in physique fluids or excretory merchandise. For bioavailability and bioequivalence studies, both the father or mother drug and its main active metabolites are usually measured. Measurement of the lively metabolite is important for very high-hepatic clearance (first-pass metabolism) medication when the father or mother drug concentrations are too low to be dependable. The analytical methodology for measurement of the drug should be validated for accuracy, precision, sensitivity, specificity, and robustness. The use of multiple analytical technique throughout a bioequivalence study will not be legitimate, as a outcome of different methods could yield totally different values. The plasma drug concentration�time curve for every drug product and each topic must be obtainable. Fasting Study Bioequivalence research are usually evaluated by a single-dose, two-period, two-treatment, two-sequence, open-label, randomized crossover design comparing equal doses of the take a look at and reference merchandise in fasted, grownup, healthy topics. This study is requested for all immediate-release and modified-release oral dosage varieties. Blood sampling is carried out just earlier than (zero time) the dose and at applicable intervals after the dose to get hold of an enough description of the plasma drug concentration�time profile. The topics must be within the fasting state (overnight quick of at least 10 hours) before drug administration and should continue to quick for up to four hours after dosing.
Syndromes - Vomiting blood
- Sunken eyes
- Men: above 40 mg/dL
- Cervical cultures to check for a sexually transmitted infectin
- Your doctor may refer you for physical therapy. The physical therapist will help you try to reduce your pain, using stretches. The therapist will show you how to do exercises that make your neck muscles stronger.
- Narrowing of other arteries in the body, such as to the legs, the brain, the eyes and elsewhere
The primary part of the requirement is the reporting of adverse drug experiences. This is completed by reassessing drug risks based mostly on information realized after the drug is marketed. For example, a brand new opposed reaction mentioned by postmarketing surveillance is required for each branded and generic drug merchandise. Impact of Biopharmaceutics on Drug Product Quality and Clinical Efficacy 563 Continuous course of verification: An different strategy to course of validation in which manufacturing course of efficiency is continuously monitored and evaluated. Design area: the multidimensional combination and interplay of enter variables (eg, materials attributes) and process parameters which have been demonstrated to present quality assurance. Movement out of the design house is taken into account to be a change and would normally provoke a regulatory postapproval change course of. Design area is proposed by the applicant and is topic to regulatory assessment and approval. Formal experimental design: A structured, organized technique for figuring out the connection between elements affecting a process and the output of that course of. Process robustness: Ability of a process to tolerate variability of supplies and adjustments in the process and equipment without adverse influence on high quality. Quality: the suitability of either a drug substance or a drug product for its intended use. Quality by design (QbD): A systematic strategy to improvement that begins with predefined objectives and emphasizes product and course of understanding and process management, based mostly on sound science and quality threat administration. Drug product quality and drug product efficiency are essential for affected person security and therapeutic efficacy. Drug product quality and drug product efficiency relate to the biopharmaceutic and physicochemical properties of the drug substance and the drug product and to the manufacturing course of. The growth of a drug product requires a scientific, scientific, risk-based, holistic, and proactive approach that begins with predefined aims and emphasizes product and processes understanding and course of management (QbD). Product high quality defects are controlled through Good Manufacturing Practices, monitoring, and surveillance. The want for "be taught and confirm" is a crucial approach evaluating completely different high quality methods balancing threat and need for progress. Three batches of ibuprofen tablets, 200 mg, are manufactured by the same manufacturer using the same gear. Does meeting specs imply that each batch of drug product contains the identical quantity of ibuprofen What should a manufacturer of a modifiedrelease tablet think about when making a qualitative or quantitative change in an excipient For strong oral drug merchandise, a change in the focus of which of the next excipients is extra more likely to influence the bioavailability of a drug How does the polymorphic form of the active drug substance influence the bioavailability of a drug Can two totally different polymorphs of the identical active drug substance have the same bioavailability Thus, one batch of nominally 200-mg ibuprofen tablets may comprise an average content material of 198 mg, whereas the typical content material for an additional batch of 200-mg ibuprofen tablets may have a median content of 202 mg. Both batches meet a specification of �5% and could be thought of to meet the label declare of 200 mg of ibuprofen per tablet. What ought to a producer of a modified-release pill consider when making a qualitative or quantitative change in an excipient A qualitative change within the excipient may have an effect on drug release and thus will have important effect on the formulation efficiency. Selen A, et al: the biopharmaceutics threat evaluation roadmap for optimizing clinical drug product efficiency. Shargel L: Drug product performance and interchangeability of multisource drug substances and drug products. This page intentionally left clean 19 Chapter Objectives �� �� Modified-Release Drug Products and Drug Devices Hong Ding Define modified-release drug products. Differentiate between typical, immediaterelease, extended-release, delayed-release, and targeted drug merchandise. Describe the kinetics of extended-release drug merchandise in comparability with immediate-release drug merchandise. Explain when an extendedrelease drug product should contain an immediate-release drug dose. Explain why extended-release beads in capsule formulation might have a unique bioavailability profile in comparability with an extended-release pill formulation of the same drug. Describe several approaches for the formulation of an oral extended-release drug product. Explain why a transdermal drug product (patch) could additionally be considered an extended-release drug product. In the formulation of typical drug merchandise, no deliberate effort is made to modify the drug launch price. In the case of typical oral merchandise containing prodrugs, the pharmacodynamic activity may be altered as a result of the time consumption with conversion from prodrugs to the active drug by hepatic or intestinal metabolism or by chemical hydrolysis. A modified-release dosage kind is a formulation by which the drug-release characteristics of time course and/or location are chosen to accomplish therapeutic or 567 �� �� �� �� �� �� 568 �� Chapter 19 Describe the elements of a transdermal drug supply system. Explain why an extended-release formulation of a drug could have a special efficacy profile in comparability with the same dose of drug given in as a standard, immediate-release, oral dosage type in multiple doses. List the research that may be required for the development of an extended-release drug product. List the several achievements on the drug devices primarily based on the modified-release drug design. A dosage kind that allows a minimal of a twofold discount in dosage frequency as compared to that drug presented as an immediate-release (conventional) dosage kind. Examples of extended-release dosage varieties include controlled-release, sustained-release, and long-acting drug merchandise. A dosage type that releases a discrete portion/portions of drug at a time other than the promptly release after administration. A dosage form that releases drug at or near the meant physiologic web site of action (see Chapter 20). Targeted-release dosage forms may have either immediate- or extended-release characteristics. The time period controlled-release drug product was previously used to describe numerous forms of oral extended-release-rate dosage forms on the action agency utilized, together with sustained-release, sustainedaction, prolonged-action, long-action, slow-release, and programmed drug supply. Many of these phrases for modified-release drug merchandise had been introduced by drug companies to replicate a particular design both for an extended-release drug product or to be used in advertising. Several different terms are now defined to describe the available kinds of modified-release drug merchandise based on the drug release characteristics of the merchandise. Fentanyl citrate is within the form of a flavored sugar lozenge that dissolves slowly within the mouth. Basulin is a controlled-release, recombinant human insulin delivered by nanoparticulate technology. Liposomal preparation to maximize the selectivity of daunorubicin for strong tumors in situ. Implant designed to ship carmustine directly into the surgical cavity when a mind tumor is resected. Sterile implant designed to release fluocinolone acetonide domestically to the posterior phase of the attention. New and novel drug supply techniques are being developed by the pharmaceutical industry to alter the drug release profile, which in turn leads to a unique plasma drug concentration-versus-time profile and pharmacodynamic impact. An enteric-coated tablet is one sort of delayedrelease sort throughout the modified-release dosage household designed to launch drug in the small intestine. Different from the movie coating on tablets or capsules to forestall bitter taste from medicine or shield tablets from microbial growth as properly as shade alteration, normally the enteric-coating materials are polymer-based barrier applied on oral medicine. This coating might delay launch of the medicine until after it leaves the abdomen, both for the purpose of drug protection under harsh pH circumstance or for alleviation of irritation on cell membrane from the drug itself. Then the enteric coating on the aspirin tablet may forestall the pill from disintegration promptly and releasing its contents on the low pH in the abdomen.
[newline]The coating and the tablet later dissolve and launch the drug within the relative gentle pH of the duodenum, the place the drug is quickly absorbed with much less irritation to the mucosal cells.
Syndromes - Color vision
- Lack of blood flow to the liver (liver ischemia)
- The person loses consciousness at any time.
- Chest x-ray
- Scalp defects (missing skin)
- Difficulty focusing on near objects
- Heartburn
Capacity-limited processes for medicine embrace: � Absorption Active transport Intestinal metabolism by microflora � Distribution Protein binding � Elimination Hepatic elimination Biotransformation Active biliary secretion � Renal excretion Active tubular secretion Active tubular reabsorption 0 4. In dosing, medication are given in milligrams and plasma drug concentrations are expressed as milligrams per liter or micrograms per milliliter. They are due to this fact commonly expressed as milligrams per liter, which is preferred over micrograms per milliliter as a end result of dose is often expressed in milligrams. Clinical features of 8295 patients with resistant hypertension classified on the idea of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Hashimoto Y, Odani A, Tanigawara Y, Yasuhara M, Okuno T, Hori R: Population analysis of the dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of zonisamide in epileptic patients. Hashimoto Y, Koue T, Otsuki Y, Yasuhara M, Hori R, Inui K: Simulation for inhabitants analysis of Michaelis�Menten kinetics. Lemmer B: the significance of circadian rhythms on drug response in hypertension and coronary heart disease-From mice and man. Von Roemeling R: the therapeutic index of cytotoxic chemotherapy depends upon circadian drug timing. A pharmacokinetic study of the simultaneous conjugation of benzoic and salicylic acids with glycine. Mehvar R: Principles of nonlinear pharmacokinetics: Am J Pharm Edu 65:178�184, 2001. Wagner J: Properties of the Michaelis�Menten equation and its integrated kind that are useful in pharmacokinetics. The drug molecules are carried by the blood to the target web site (receptor) for drug motion and to other (nonreceptor) tissues as properly, the place side effects or antagonistic reactions could happen. Drug molecules are distributed to eliminating organs, such as the liver and kidney, and to noneliminating tissues, such as the mind, skin, and muscle. Drugs can also be secreted in milk by way of the mammillary glands, into the saliva and into different secretory pathways. A substantial portion of the drug could also be sure to proteins within the plasma and/or in the tissues. Drug distribution all through the body occurs primarily by way of the circulatory system, which consists of a series of blood vessels that carry the drug in the blood; these embrace the arteries that carry blood to tissues, and the veins that return the blood back to the heart. The volume of blood pumped by the center per minute-the cardiac output-is the product of the stroke quantity of the heart and the variety of heartbeats per minute. Left ventricular contraction may produce a systolic blood stress of a hundred and twenty mm Hg, and moves blood at a linear speed of 300 mm/s through the aorta. Drug molecules rapidly diffuse by way of a community of fantastic capillaries to the tissue spaces 259 Describe the physiology of drug distribution within the physique. Explain how drug distribution is affected by blood flow, protein, and tissue binding. Explain how quantity of distribution, drug clearance, and half-life may be affected by protein binding. Evaluate the influence of change in drug�protein binding or displacement on free drug focus. The interstitial fluid plus the plasma water is termed extracellular water, because these fluids reside outside the cells. Drug molecules may further diffuse from the interstitial fluid throughout the cell membrane into the cell cytoplasm. Drug distribution is generally fast, and most small drug molecules permeate capillary membranes simply. The passage of drug molecules across a cell membrane depends on the physicochemical nature of each the drug and the cell membrane. Cell membranes are composed of protein and a bilayer of phospholipid, which act as a lipid barrier to drug uptake. Thus, lipid-soluble medication generally diffuse throughout cell membranes more easily than extremely polar or water-soluble drugs. Small drug molecules usually diffuse extra quickly throughout cell membranes than giant drug molecules. If the drug is sure to a plasma protein such as albumin, the drug�protein advanced becomes too large for straightforward diffusion across the cell or even capillary membranes. A comparability of diffusion rates for water-soluble molecules is given in Table 11-1. Diffusion and Hydrostatic Pressure the processes by which medication transverse capillary membranes into the tissue include passive diffusion and hydrostatic pressure. The unfavorable sign denotes web transfer of drug from contained in the capillary lumen into the tissue and extracellular spaces. Diffusion is distinguished from blood flow�initiated mixing, which involves hydrostatic pressure. Hydrostatic pressure is responsible for penetration of water-soluble medication into spaces between endothelial cells and presumably into lymph. In the kidneys, excessive arterial pressure creates a filtration Rate of drug diffusion pressure that allows small drug molecules to be filtered within the glomerulus of the renal nephron (see Chapter 7). Blood flow�facilitated drug distribution is fast and efficient, but requires strain. As blood stress progressively decreases when arteries branch into the small arterioles, the speed of move slows and diffusion into the interstitial house becomes diffusion or focus pushed and facilitated by the massive surface space of the capillary network. The common stress of the blood capillary is greater (+18 mm Hg) than the mean tissue stress (-6 mm Hg), leading to a web whole pressure of 24 mm Hg higher within the capillary over the tissue. This stress difference is offset by a median osmotic pressure in the blood of 24 mm Hg, pulling the plasma fluid back into the capillary. Thus, on common, the pressures within the tissue and most components of the capillary are equal, with no web circulate of water. The decrease pressure of the venous blood in contrast with the tissue fluid is termed as absorptive pressure. Kinetically, if a drug diffuses rapidly throughout the membrane in such a way that blood circulate is the ratelimiting step in the distribution of drug, then the process is perfusion or flow restricted. A individual with congestive coronary heart failure has a decreased cardiac output, leading to impaired blood circulate, which can reduce renal clearance via lowered filtration stress and blood move. Drugs which are permeability restricted might have an increased distribution volume in illness circumstances that cause inflammation and increased capillary membrane permeability. The delicate osmotic strain balance could additionally be altered as a end result of adjustments in albumin stage and/or blood loss or as a outcome of adjustments in Organ Ca Ct R Cv Ca Organ Ct R Cv electrolyte ranges in renal and hepatic ailments, resulting in net circulate of plasma water into the interstitial space (edema). This change in fluid distribution could partially explain the elevated extravascular drug distribution throughout some illness states. Blood move, tissue dimension, and tissue storage (partitioning and binding) are also essential in determining the time it takes the drug to turn out to be completely distributed. Table 11-2 lists the blood circulate and tissue mass for lots of tissues in the human body. Drug affinity for a tissue or organ refers to the partitioning and accumulation of the drug in the tissue. The time for drug distribution is usually measured by the distribution half-life or the time for 50% drug distribution. Right panel for tissue with speedy permeability; Left panel for tissue with gradual permeability. Physiologic Drug Distribution and Protein Binding 263 partitioning of the drug into the organ tissue, as proven in Equation 11. The distribution half-life of the drug to the tissue, td1/2, could simply be determined from the distribution fixed in the equation of td1/2 = zero. The ratio R is usually estimated based on data of the partition coefficient of the drug. The partition coefficient is a physical property that measures the ratio of the solubility of the drug in the oil part to solubility in aqueous section. The partition coefficient is likely considered one of the most essential components that decide the tissue distribution of a drug. If each tissue has the identical capability to retailer the drug, then the distribution half-life is ruled by the blood flow, Q, and volume (size), V, of the organ. In this illustration, the blood drug concentration is equally maintained at one hundred mg/ mL, and the drug is assumed to have equal distribution between all of the tissues and blood, i.
|
|