|
"Biaxin 250 mg mastercard, gastritis diet чат". K. Yokian, MD Co-Director, Weill Cornell Medical College
These skills include a minimum of 50 hours of driving experience in various terrain and conditions and complete knowledge of harness and vehicle terminology gastritis diet book discount biaxin 250 mg with mastercard, competencies in managing emergencies gastritis diet танки order 250mg biaxin with visa. A header is required while the equine is being put to or taken from the vehicle gastritis nursing care plan biaxin 500mg line, while participant is entering or exiting the vehicle and available whenever assistance with the equine is needed chronic gastritis for years purchase biaxin 500mg mastercard. Standards for Certification & Accreditation 2018 157 Glossary of Medical Terms the following terms may be found elsewhere in this manual, or they are terms that may be used in reference to participants at a Professional Association of Therapeutic Horsemanship International Center (for example, on the medical history forms). Additional information can be obtained in medical dictionaries, reference texts, on the Internet or from professionals such as doctors, pharmacists, therapists or mental health professionals. This is a classification manual of mental disorders that includes descriptions of diagnostic categories. The Diagnostic & Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is the most widely accepted system of classifying abnormal behaviors used in the United States today. Examples include grooming, bathing, dressing, using the telephone, preparing meals, cleaning house, taking medicines, doing laundry, handling finances, getting to the bus stop and shopping at the grocery. For example, a client may be said to have a flat affect, meaning that there is an absence or a near absence of facial expression when there is an experience or emotion that would usually cause an emotional response. For example, a person may be unable to identify familiar sounds, such as the ringing of a doorbell (auditory agnosia), or familiar objects, such as a toothbrush or keys (visual agnosia). For example, a person may be unable to shave, to dress, or to do other previously learned and purposeful tasks. Examples of behavioral therapy techniques include operant conditioning, token economy, systematic desensitization, aversion therapy and flooding. This abnormality can cause hydrocephalus, severe headaches and a variety of other neurological symptoms. This condition is due to shortening of muscles, tendons and/or ligaments around joints. This response is useful in emergencies; however, a sustained response can result in pathophysiological changes such as high blood pressure, ulcers, cardiac problems and more. Manipulation is maladaptive when: 1) it is the primary method used for getting needs met; 2) the needs, goals and feelings of others are disregarded; and 3) others are treated as objects in order to fulfill the needs of the manipulator. Behavior may seem passive but is motivated by unconscious anger, often triggering anger and frustration in others. Disturbance of perception is an inability to register and interpret sensory stimuli based on past experiences. The term is used in reference to certain diseases thought to be caused by psychological factors. The degree of stiffness is velocity dependent; the more quickly a muscle is stretched, the stiffer it becomes.
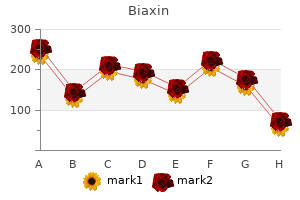
Next gastritis symptoms upper abdomen biaxin 500mg with visa, increased right hypertropia in contralateral gaze narrows the possibilities to right superior oblique or left superior rectus weakness gastritis diet 600 buy biaxin 250 mg visa. Fluorescein angiogram (B gastritis diet 4 you cheap 500 mg biaxin with amex, D) shows optic nerve hyperfluorescence bilaterally (arrows) with left stippled hypofluorescent spots representing choroidal leakage with nonfilling infiltrates (D xeloda gastritis biaxin 500 mg with amex, asterisk). He denied any symptoms of raised intracranial pressure including headSupplemental data at Two months prior, he developed pain in his lower back radiating into both legs and an associated band-like sensation around his waist. Ophthalmoscopy showed marked bilateral optic disc swelling (figure 1, A and C) and macular edema in the left eye. Visual field testing showed a small inferotemporal scotoma in the right eye, with a larger central scotoma in the left eye. There was subjective decrease in light touch and pinprick sensations up to the midshin level bilaterally. However, uncomplicated papilledema is not typically associated with reduced visual acuity or dyschromatopsia. Lymphoma can also invade the meninges, producing multiple cranial neuropathies and polyradiculopathies. This patient had a history suggestive of prior polyradiculopathy, but the spontaneous resolution of his symptoms was atypical of lymphoma. Infections such as cryptococcus, toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis, herpes zoster, cytomegalovirus, and herpes simplex virus can also affect the optic nerves or the retina. There was no evidence of venous sinus thrombosis or abnormal meningeal enhancement. Lumbar puncture yielded a slightly high opening pressure (27 cm H2O), high white cell count (21. However, the opening pressure associated with these conditions is typically much higher than that observed in this case. To better tailor further workup, reconsideration of the localization of the problem is important. Processes affecting the afferent visual pathway posterior to the chiasm should produce visual field deficits that respect the vertical meridian in both eyes. The field defects in this case crossed the vertical meridian, indicating a process affecting the visual pathway anterior to the chiasm. Therefore, given the lateralizing defects in visual acuity, visual field sensitivity, and color vision in the left eye, further assessment of the anterior and posterior segments, with focused examination of the macular regions, is necessary to identify any pathology and to elucidate the mechanism of vision loss in this case. In addition to the optic disc edema, there was a slightly creamy appearance to the choroid around the disc, greater in the left than the right eye. Fluorescein angiogram showed an infiltrative process around the optic nerves in both eyes, and extension through the macula in the left eye (figure 1, B and D). Further testing showed a reactive plasma syphilis antibody that was confirmed with enzyme immunoassay. Although syphilis serology does not differentiate active disease from previous infection, this man was known to have unreactive syphilis testing in the recent past. He was treated with parenteral penicillin with significant improvement in his visual symptoms. When assessed in follow-up after 2 months, his visual acuity was 20/20 in both eyes. Fundus examination demonstrated mild optic disc hyperemia bilaterally (figure e-1 on the Neurology Web site at In the early infection phase, acute meningitis, meningovasculitis, and myelitis have been described. Cognitive impairment (general paralysis of the insane) and tabes dorsalis, characterized by sensory ataxia and lancinating pains, are seen in the late stages of the disease. This can pose a challenge in the immunocompromised patient since serology relies on the immune response to the infection. Williams serves on scientific advisory boards for Bausch Lomb, Novartis, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. She reported 3 weeks of progressive clumsiness of the right limbs, weakness of the right leg, and an unsteady gait.
A "toxoid" is a denatured (nonpathogenic) toxin which stimulates an immune response against the toxin but not necessarily the organism as a whole chronic gastritis support group buy biaxin 250mg visa. Immunization promotes an antibody response that neutralizes the exotoxin gastritis diet цитаты buy biaxin 500mg otc, protecting against the cardiotoxic and neurotoxic effects of the exotoxin which is produced during infection gastritis definition cause biaxin 250 mg amex. A reduced diphtheria-antigen adult formulation booster (dT) is administered at 11-12 years bile gastritis diet buy cheap biaxin 250 mg, and subsequent boosters are then administered at 10 year intervals throughout life. Tetanus (T) vaccine is a toxoid vaccine that provides formalin-inactivated tetanus toxin, derived from the neuromuscular toxin tetanospasmin produced by Clostridium tetani (3). Persons who sustain injuries more likely to become infected with Clostridium tetani (crush wounds with devitalized tissue, deep puncture wounds, wounds contaminated with soil or vegetative matter) should receive a booster dose of tetanus vaccine if at least 5 years have passed since last receiving a tetanus vaccine booster. The most common adverse reactions to tetanus immunization are fever and local reactions at the injection site. Severe allergic reactions, Guillain-Barre syndrome, and brachial neuritis occur rarely. Three acellular pertussis (aP) vaccines are currently licensed and available for use in the United States (Tripedia, Infanrix, Daptacel). These vaccines are called acellular, to distinguish this formulation from the older whole-cell pertussis vaccine. Whole-cell pertussis vaccine consisted of inactivated ("killed") but otherwise complete Bordetella pertussis bacteria. Administration provided protection against disease but was associated with the potential for adverse effects that occurred frequently and could be quite severe on rare occasion. In order to provide a vaccine that was better tolerated, individual bacterial components that contributed to organism virulence and pathogenicity were identified and purified as individual cell-free (acellular) antigens that comprise the current acellular pertussis vaccines (3,5). Whole-cell pertussis vaccine was not provided to persons beyond 7 years old, due to the Page - 25 increased incidence of adverse reactions associated with immunization. Currently, acellular pertussis vaccine is not recommended for immunization of persons older than 7 years of age due to the prior experience of whole-cell pertussis vaccine in this age group, although research is currently being conducted to see if adults may safely receive booster doses of the less reactogenic acellular pertussis vaccine to enhance and extend immunity to pertussis. The most common adverse reactions to acellular pertussis immunization are fever and local reactions at the injection site. Rare but potentially serious reactions, including high fevers, prolonged crying, hypotonic-hyporesponsive episodes, and seizures have occurred, but at significantly lower frequency than was true for whole cell pertussis vaccine. Immunization effectively protects against paralytic poliomyelitis, but may not protect against subclinical enteric infection due to lack of secretory antibody response to inactivated polio vaccine (6). Inactivated polio vaccine is administered as a 4 dose regimen by intramuscular injection at 2 months, 4 months, between 6 months and 15 months (3 dose primary series), and between 4 years and 6 years of age (booster dose). The most common adverse reactions to inactivated polio immunization are fever and local reactions at the injection site. Inactivated polio vaccine cannot cause vaccine associated paralytic poliomyelitis. In addition, oral polio vaccine uniquely protects against enteric infection by promoting mucosal immunity and offering the benefit of herd immunity by secondary immunization of susceptible persons exposed to asymptomatic shedding of vaccine strain virus from vaccine recipients. Unfortunately, as paralytic poliomyelitis due to wild-type virus was eradicated in the United States by effective immunization programs, the rare risk of paralytic poliomyelitis due to vaccine strain virus (3 to 12 cases annually) ultimately has become greater than the risk due to wild-type poliovirus. Therefore, only inactivated polio vaccine is used in the United States currently, whereas the effective, economically favorable, convenient trivalent oral polio vaccine continues to be used in wild-virus polio endemic regions in an attempt to eradicate paralytic poliomyelitis worldwide. The four monovalent conjugated Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccines currently available are differentiated by their respective carrier proteins. Infants receive either a 2 dose or 3 dose series of Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine during the first year of life (predicated by specific vaccine brand utilized), and a single booster dose between 12 months and 15 months of age (resulting in either a 3 dose or 4 dose regimen to completely immunize the child). The number of conjugated Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine doses required to immunize older children not receiving vaccine in infancy diminishes due to brisker antibody response seen when older children receive conjugated Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine. If the first dose of vaccine is not administered until the child is between 12 months and 14 months of age, then only 2 doses are required to complete the regimen. If the first dose of vaccine is not administered until the child is between 15 months and 59 months of age, then only a single dose is required to complete the regimen. Non-immunized children 5 years old and older do not require Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine unless they possess underling risk factors (impairment in immunity) that would increase their risk for invasive disease. The most common adverse reactions to conjugated Haemophilus influenzae type b immunization are fever and local reactions at the injection site. Each specific polysaccharide is conjugated with a nontoxic mutant diphtheria toxin to enhance immunogenicity when administered to infants.
Without the opposing pressure gastritis tea biaxin 500mg mastercard, the gas under this pressure is forced out of the alveolus gastritis vomiting cheap 500mg biaxin mastercard. If the alveolus is connected to an adjacent alveolus with a larger radius gastritis diet pregnancy generic biaxin 250 mg line, air will preferentially inflate the larger alveolus and ultimately collapse the smaller alveolus gastritis diet лего discount biaxin 250mg online. This leads to the network of air-filled alveoli juxtaposed to atelectatic alveoli and creates the reticulogranular pattern (ground glass appearance) of the lung. The air bronchograms are created by atelectatic alveoli outlining the adjacent rigidly distended airways. The phospholipids and surfactant related proteins, contained in surfactant, spread along the air liquid interface to decrease alveolar surface tension. Furthermore, the surfactant molecules contribute to the larger alveoli developing a higher surface tension during inspiration and a lower surface tension (as the alveoli deflate) during expiration when the surfactant molecules become more compact along the air liquid interface. Today, several types of animal based surfactants have been approved for clinical use. High frequency ventilation has been shown to improve the short term management of these infants. Page - 92 Moderately premature infants (29 to 34 weeks gestation) are usually extubated within several days after treatment. However, extremely premature infants (23 to 28 weeks gestation) may continue to require positive pressure respiratory support for several weeks. They are at high risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia or chronic respiratory insufficiency of the premature. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is the chronic lung disease consequence of early acute lung disease and/or lung immaturity of the premature infant. Chronic respiratory insufficiency of the premature develops despite early improvement after surfactant therapy and mechanical ventilation. However, premature infants have at least a 10 fold increased incidence of infections when compared to term infants. Mothers with intrapartum fever and prolonged rupture of membranes (>18-24 hours) have a greater risk of transmitting infections to their infants. Infected infants present either immediately after birth with respiratory distress or they may present after several hours of an asymptomatic period. Due to the serious consequences associated with delays in treatment for infections, many infants with non-infectious conditions are evaluated and empirically treated with antibiotics for this possibility. A left shift with greater than 20% band forms of the total neutrophils is suggestive of infection as are neutrophilic vacuoles and toxic granulation. The gold standard still remains the blood culture or culture of lung and tracheal secretions. Treatment with an aminoglycoside and penicillin is standard to treat for the common organisms. Supportive care may include mechanical ventilation, supplemental oxygen, inotropic agents for hypotension and nitric oxide for infection associated pulmonary hypertension. The mortality from infections has decreased from 50% to 20% with more aggressive intensive care. Some congenital malformations of the cardiopulmonary system will be addressed here. Most infants with transposition of the great arteries, tetralogy of Fallot and hypoplastic right and left heart syndromes, will present in the newborn period. Most infants with cyanotic heart disease typically have a paucity of respiratory distress symptoms except for cyanosis or duskiness. Typically the chest radiograph reveals a normal sized heart or cardiomegaly with clear lung fields and decreased vascular markings (due to diminished pulmonary blood flow). When the infant develops respiratory symptoms, it is usually from severe hypoxemia or acidosis. The infant who is cyanotic with respiratory distress and does not respond to supplemental oxygen (i. Infants with both cyanosis and respiratory distress may have chest radiographs typical of pulmonary disease. The hyperoxy test (measuring the arterial pO2 while the infant is breathing 100% oxygen) is helpful in distinguishing cyanotic heart disease from severe respiratory disease. The echocardiogram is also diagnostic and will distinguish between cyanotic heart disease and persistent pulmonary hypertension.
|
|