|
"Buy cheap duetact 16 mg online, diabete x quiabo". H. Kaelin, MD Deputy Director, University of Texas at Tyler
These abnormal mitochondria may result in the histologic appearance of the muscle as ragged red fibers diabetes in dogs skin problems generic duetact 16mg with amex. Electron microscopy reveals the presence within large mitochondria of rectangular crystals that have a "parking lot" appearance diabetes signs of diabetes buy generic duetact 16 mg on-line. Some types of sphingolipids are typically found within the central nervous system diabetes 800 purchase duetact 16mg without prescription, and therefore abnormal accumulation of these substances produces neurologic signs and symptoms diabetes signs in young adults buy duetact 17mg without a prescription. For example, ganglion cells within the retina, particularly at the periphery of the macula, may become swollen with excess sphingolipids. The affected area of the retina appears pale when viewed through an ophthalmoscope. In contrast, the normal color of the macula, which does not have accumulated substances, appears more red than normal. Autosomal recessive disorders tend to be more common in areas in which inbreeding is more common. An example of this is the increased frequency of several autosomal recessive genes in Ashkenazi Jews. Ashkenazi denotes an ethnic group, mostly of the Jewish faith, from Eastern Europe. Two storage diseases that have a higher incidence in Ashkenazi Jews are Tay-Sachs disease and type I Gaucher disease. General Pathology Answers 87 Patients with Tay-Sachs disease have a deficiency of the subunit. There are several clinical forms of Tay-Sachs disease, but the most severe is the infantile type. Patients develop mental retardation, seizures, motor incoordination, and blindness (amaurosis), and usually die by the age of 3 years. Patients may have increased serum levels of acid phosphatase (an enzyme that is typically found in the prostate), erythrocytes, and platelets. Several of these biochemical steps involve transferring methyl groups from folate. This disorder is characterized by excess uric acid production, which may produce symptoms of gout, mental retardation, spasticity, self-mutilation, and aggressive behavior. The extra X is from the mother in most cases, and therefore this disorder is associated with increased maternal age. The hypogonadism causes decreased testosterone levels, which leads to eunuchoidism, lack of secondary male characteristics, and a female distribution of hair. Patients are tall due to delayed fusion of the epiphysis from a lack of testosterone. Patients also develop a high voice and gynecomastia, and they have an increased incidence of breast cancer. Patients have small, firm, atrophic testes, histologic sections of which reveal atrophy, Leydig cell hyperplasia, sclerosis of the tubules, and lack of sperm production. The fragile X syndrome, which is more common in males than females, is one of the most common causes of familial mental retardation. Additional clinical features of this disorder include developmental delay, a long face with a large mandible, large everted ears, and large testicles (macroorchidism). Normally these repeats average up to 50 in number, but in patients with fragile X syndrome there are more than 230 repeats. During oogenesis, but not spermatogenesis, premutations can be converted to mutations by amplification of the triplet repeats. An additional finding associated with these repeat units is anticipation, which refers to the fact that the disease is worse in subsequent generations. Glomerular lesions are very rare, but a mild tubulointerstitial nephritis is quite common and may result in renal tubular acidosis. In addition to the usual dense, lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate of salivary glands, the lymph nodes may show a "pseudolymphomatous" appearance. This abnormality results from defective maturation of B lymphocytes beyond the pre-B stage.
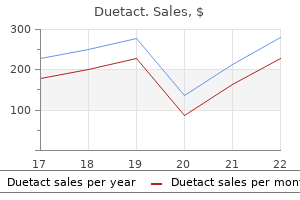
Much of the acetyl-CoA is used to synthesize ketone bodies (essentially 2 acetyl-CoA groups linked together) that are released into the blood for other tissues diabetes test rite aid buy duetact 17 mg with amex. Decreased acetyl-CoA lowers pyruvate carboxylase activity and also limits ketogenesis test x180 and diabetes purchase 17mg duetact otc. After a period of prostration that may last as long as 18 hours diabetes signs the honeymoon is over purchase duetact 17 mg amex, more vomiting may occur diabetes mellitus other names discount duetact 17 mg fast delivery, followed by convulsions, coma, and even death. The presence of severe hypoglycemia and absence of ketosis (hypoketosis) is strongly suggestive of a block in -oxidation. The episode in this case was precipitated by the 3-day gastroenteritis (vomiting/fasting). Because this extra succinyl-CoA can form malate and enter the cytoplasm and gluconeogenesis, odd-carbon fatty acids represent an exception to the rule that fatty acids cannot be converted to glucose in humans. In a patient with megaloblastic anemia, it is important to determine the underlying cause because B12 deficiency, if not corrected, produces a peripheral neuropathy owing to aberrant fatty acid incorporation into the myelin sheets associated with inadequate methylmalonyl-CoA mutase activity. Excretion of methylmalonic acid indicates a vitamin B12 deficiency rather than folate. Cardiac and skeletal muscles and renal cortex metabolize acetoacetate and 3-hydroxybutyrate to acetyl-CoA. Normally during a fast, muscle metabolizes ketones as rapidly as the liver releases them, preventing their accumulation in blood. After a week of fasting, ketones reach a concentration in blood high enough for the brain to begin metabolizing them. Ketogenesis (Liver) and Ketogenolysis (Extrahepatic) Clinical Correlate In untreated type 1 diabetes mellitus, there is no insulin. Acetone is a minor side product formed nonenzymatically but is not used as a fuel in tissues. This important switch spares body protein (which otherwise would be catabolized to form glucose by gluconeogenesis in the liver) by allowing the brain to indirectly metabolize fatty acids as ketone bodies. Glycogen Protein Fat (minor protein component) 100 Glucose from gluconeogenesis % of Fuel for Brain Ketones 50 Glucose from liver glycogen Ketones 1 2 3 4 1 2 Glucose from gluconeogenesis 3 4 5 6 Days Weeks Figure I-16-5. The basis for this observation is not completely understood, although type 2 disease has a much slower, insidious onset, and insulin resistance in the periphery is usually not complete. Chronic hypoglycemia, which is often present in chronic alcoholism, favors fat release from adipose. Ketone production increases in the liver, but utilization in muscle may be slower than normal because alcohol is converted to acetate in the liver, diffuses into the blood, and oxidized by muscle as an alternative source of acetyl-CoA. Once insulin is administered, however, blood potassium levels need to be monitored. In normal ketosis (which accompanies fasting and does not produce an acidosis), acetoacetate and -hydroxybutyrate are formed in approximately equal quantities. In pathologic conditions such as diabetes and alcoholism, ketoacidosis may develop with life-threatening consequences. In diabetic and alcoholic ketoacidosis, the ratio between acetoacetate and -hydroxybutyrate shifts, and -hydroxybutyrate predominates. Home monitors of both blood glucose and -hydroxybutyrate are available for diabetic patients. Carnitine acyltransferase-1 Carnitine acyltransferase-2 Medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase E. The various classes of sphingolipids differ primarily in the nature of the hydrophilic region. Lysosomes contain many enzymes, each of which removes specific groups from individual sphingolipids. The attending physician noted massive hepatomegaly and splenomegaly, marked pallor, and hematologic complications.
The vitamin is widely distributed in all food-stuffs diabetes test results table generic duetact 16mg with amex, and deficiency has not been unequivocally reported in humans except in specific depletion studies diabetes prevention natural remedies order duetact 16mg otc. This glycine is hydroxylated on the -carbon by a copper-containing enzyme diabetes insipidus pathophysiology buy duetact 17 mg cheap, peptidylglycine hydroxylase diabetes test in pregnancy buy duetact 16mg fast delivery, which, again, requires ascorbate for reduction of Cu2+. A number of iron-containing, ascorbate-requiring hydroxylases share a common reaction mechanism, in which hydroxylation of the substrate is linked to decarboxylation of -ketoglutarate. Proline and lysine hydroxylases are required for the postsynthetic modification of procollagen to collagen, and proline hydroxylase is also required in formation of osteocalcin and the C1q component of complement. Trimethyllysine and -butyrobetaine hydroxylases are required for the synthesis of carnitine. Foods grown on soil containing high levels of selenium cause toxicity, and excessive intakes of sodium cause hypertension in susceptible people. However, in addition to its other roles, vitamin C enhances the absorption of iron, and this depends on the presence of the vitamin in the gut. There is very little good evidence that high doses of vitamin C prevent the common cold, although they may reduce the duration and severity of symptoms. The amounts required vary from grams per day for sodium and calcium, through milligrams per day (eg, iron, zinc), to micrograms per day for the trace elements. In general, mineral deficiencies occur when foods come from one region where the soil may be deficient in some minerals (eg, iodine and selenium, deficiencies of both of which occur in many areas of the world); when foods come from a variety of regions, mineral deficiency is less likely to occur. However, iron deficiency is a general problem, because if iron losses from the body are relatively high (eg, from heavy Vitamins are organic nutrients with essential metabolic functions, generally required in small amounts in the diet because they cannot be synthesized by the body. The lipidsoluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) are hydrophobic molecules requiring normal fat absorption for their absorption and the avoidance of deficiency. Vitamin A (retinol), present in meat, and the provitamin (-carotene), found in plants, form retinaldehyde, utilized in vision, and retinoic acid, which acts in the control of gene expression. Vitamin D is a steroid prohormone yielding the active hormone calcitriol, which regulates calcium and phosphate metabolism; deficiency leads to rickets and osteomalacia. Vitamin E (tocopherol) is the most important antioxidant in the body, acting in the lipid phase of membranes protecting against the effects of free radicals. Vitamin K functions as cofactor of a carboxylase that acts on glutamate residues of precursor proteins of clotting factors and bone proteins to enable them to chelate calcium. Thiamin is a cofactor in oxidative decarboxylation of -keto acids and of transketolase in the pentose phosphate pathway. Pantothenic acid is present in coenzyme A and acyl carrier protein, which act as carriers for acyl groups in metabolic reactions. Vitamin C is a water-soluble antioxidant that maintains vitamin E and many metal cofactors in the reduced state. When intake is insufficient, deficiency may develop, and excessive intakes may be toxic. Department of Health: Dietary Reference Values for Food Energy and Nutrients for the United Kingdom. Food and Nutrition Division of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization, 2000. Institute of Medicine: Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D and Fluoride. Institute of Medicine: Dietary Reference Values for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin and Choline. Institute of Medicine: Dietary Reference Values for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium and Carotenoids. Institute of Medicine: Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium and Zinc. Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition of the Food Standards Agency: Folate and Disease Prevention. They cause damage to nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids in cell membranes and plasma lipoproteins. This can cause cancer, atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease, and autoimmune diseases. Epidemiological and laboratory studies have identified a number of protective antioxidant nutrients: selenium, vitamins C and E, -carotene, and a variety of polyphenolic compounds derived from plant foods.
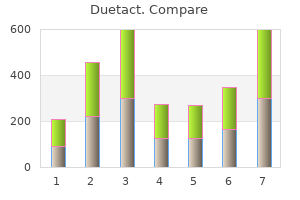
Patients receiving corticosteroids should be closely monitored for development of other opportunistic infections diabete quebec duetact 17 mg with visa. Managing Treatment Failure Brain biopsy should be considered in the event of early clinical or radiologic neurologic deterioration despite adequate empiric treatment or in children who do not clinically respond to anti-Toxoplasma therapy after 10 to 14 days diabete 0 90 order duetact 17mg. The highest risk of relapse appears to occur within the first 6 months after stopping secondary prophylaxis diabetes sweating purchase 17 mg duetact with amex. Neonatal serologic screening and early treatment for congenital Toxoplasma gondii infection diabetic diet nursing care plan duetact 17mg fast delivery. Epidemiology of congenital toxoplasmosis identified by population-based newborn screening in Massachusetts. Toxoplasma gondii infection in the United States: seroprevalence and risk factors. Mother-to-child transmission of toxoplasmosis: risk estimates for clinical counselling. Prevalence and predictors of Toxoplasma seropositivity in women with and at risk for human immunodeficiency virus infection. Vertical transmission of toxoplasma by human immunodeficiency virus-infected women. Low risk of congenital toxoplasmosis in children born to women infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Low incidence of congenital toxoplasmosis in children born to women infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Congenital toxoplasmosis occurring in infants perinatally infected with human immunodeficiency virus 1. Primary Toxoplasma gondii infection in a pregnant human immunodeficiency virus-infected woman. Congenital toxoplasmosis transmitted from an immunologically competent mother infected before conception. Primary acquired toxoplasmosis in a five-year-old child with perinatal human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Early and longitudinal evaluations of treated infants and children and untreated historical patients with congenital toxoplasmosis: the Chicago Collaborative Treatment Trial. Congenital cardiac toxoplasmosis in a newborn with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Strategy for diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis: evaluation of methods comparing mothers and newborns and standard methods for postnatal detection of immunoglobulin G, M, and A antibodies. Role of specific immunoglobulin E in diagnosis of acute toxoplasma infection and toxoplasmosis. Effect of high temperature on infectivity of Toxoplasma gondii tissue cysts in pork. Discontinuation of primary prophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and toxoplasmic encephalitis in human immunodeficiency virus type I-infected patients: the changes in opportunistic prophylaxis study. Outcome of treatment for congenital toxoplasmosis, 1981-2004: the National Collaborative Chicago-Based, Congenital Toxoplasmosis Study. Prospective randomized trial of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole versus pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine in the treatment of ocular toxoplasmosis. Immune reconstitution disease associated with parasitic infections following initiation of antiretroviral therapy. A randomized trial comparing pyrimethamine plus clindamycin to pyrimethamine plus sulfadiazine. Maintenance therapy with cotrimoxazole for toxoplasmic encephalitis in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Two doses of varicella vaccine should be given, starting as early as 12 months of age, with an interval of 3 months. Prior to the universal administration of varicella vaccine, approximately 4 million cases of varicella occurred annually in the United States. In the United States, the incidence of varicella and its associated morbidity and mortality have decreased by 88% because of universal vaccination. However, because most pregnant women have varicella immunity, varicella complicating pregnancy is unusual.
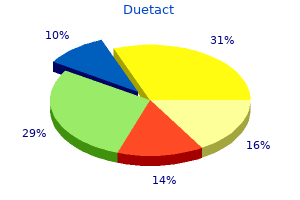
Genotype Number observed 63 28 33 77 (Number expected row total column total grand total 96 91 201 105 91 201 = 43 blood sugar level 300 order duetact 17mg with mastercard. They hypothesized that crossover events occur more or less at random up and down the chromosome and that two genes that lie far apart are more likely to undergo a crossover than are two genes that lie close together diabetic ice cream recipes purchase duetact 17 mg visa. They proposed that recombination frequencies could provide a convenient way to determine the order of genes along a chromosome and would give estimates of the relative distances between the genes diabetes type 1 feeling dizzy order duetact 16 mg line. Chromosome maps calculated by using the genetic phenomenon of recombination are called genetic maps diabetes test cork purchase duetact 17mg online. In contrast, chromosome maps calculated by using physical distances along the chromosome (often expressed as numbers of base pairs) are called physical maps. Map units are also called centiMorgans (cM), in honor of Thomas Hunt Morgan; 100 centiMorgans equals 1 Morgan. Genetic distances measured with recombination rates are approximately additive: if the distance from gene A to gene B is 5 m. B A Both maps are correct and equivalent because, with information about the relative positions of only three genes, the most that we can determine is which gene lies in the middle. If we obtained distances to an additional gene, then we could position A and C relative to that gene. An additional gene D, examined through genetic crosses, might yield the following recombination frequencies: Gene pair A and D B and D C and D Recombination frequency (%) 8 13 23 For the cell of the table corresponding to genotype y+y cv+cv (the upper-left-hand cell of the table in Figure 7. We now calculate a chi-square value by using the same formula that we used for the goodness-of-fit chi-square test in Chapter 3: x2 = (observed - expected)2 expected Recall that means "sum," and that we are adding together the (observed - expected)2/expected value for each type of progeny. With the observed and expected numbers of cockroaches from the testcross, the calculated chi-square value is 30. To determine the probability associated with this chisquare value, we need the degrees of freedom. Recall from Chapter 3 that the degrees of freedom are the number of ways in which the observed classes are free to vary from the expected values. In general, for the chi-square test of independence, the degrees of freedom equal the number of rows in the table minus 1 multiplied by the number of columns in the table minus 1 (Figure 7. This very small probability indicates that the genotypes are not in the proportions that we would expect if independent assortment were taking place. Our conclusion, then, is that these genes are not assorting independently and must be linked. As is the case for the goodness-of-fit chi-square test, geneticists generally consider that any chi-square value for the test of independence with a Linkage, Recombination, and Eukaryotic Gene Mapping 175 A A a a B B b b Double crossover 1 A single crossover will switch the alleles on homologous chromosomes. Notice that C and D exhibit the greatest amount of recombination; therefore, C and D must be farthest apart, with genes A and B between them. Two points should be emphasized about constructing chromosome maps from recombination frequencies. First, recall that we cannot distinguish between genes on different chromosomes and genes located far apart on the same chromosome. If genes exhibit 50% recombination, the most that can be said about them is that they belong to different groups of linked genes (different linkage groups), either on different chromosomes or far apart on the same chromosome. The second point is that a testcross for two genes that are far apart on the same chromosome tends to underestimate the true physical distance, because the cross does not reveal double crossovers that might take place between the two genes (Figure 7. A double crossover arises when two separate crossover events take place between two loci.
|
|