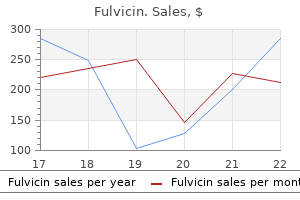
|
"Purchase fulvicin 250mg mastercard, fungus gnats indoors". H. Thorus, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D. Clinical Director, Louisiana State University School of Medicine in Shreveport
The double-pigtail ureteral stent has a pigtail coil at each end; this permits placement of the upper coil (pigtail) in the renal pelvis fungus under skin purchase 250 mg fulvicin with amex, with the lower coil at the ureteral orifice antifungal medications for dogs buy fulvicin 250 mg mastercard. The surgeon must replace the tube immediately to prevent the opening from contracting antifungal wiki generic 250mg fulvicin free shipping. Never clamp a nephrostomy tube lung fungus x ray order fulvicin 250 mg line, which could cause obstruction and resultant pyelonephritis. Encourage fluid intake to promote natural flushing of the kidney and nephrostomy tube. Using aseptic technique, apply dry dressing at nephrostomy exit site; replace dressing as needed. The bag may be disinfected and deodorized using a solution of 1 tablespoon bleach and 2 cups water. If the pleural cavity has been entered during surgery, a pneumothorax may occur, necessitating insertion of a chest tube. The incision is generally close to the diaphragm, and with a substernal incision, the nerves may be stretched and bruised. These factors can lead to pain and limited chest movement during inspiration; breathing patterns are altered or ineffective when the chest cannot fully expand. If the patient cannot generate an effective cough, either because of pain at the incision site and restricted movement or because of anesthesia, ineffective airway clearance may result. Adequate use of analgesic medications is necessary to relieve pain so that the patient can take deep breaths and cough. When the analgesia is administered at regular, frequent intervals, the patient can perform deep-breathing and coughing exercises more effectively. If undetected and untreated, bleeding can result in hypovolemia and hemorrhagic shock. Monitoring of vital signs, skin condition, urinary drainage system, surgical incision, and level of consciousness is necessary to detect evidence of bleeding, decreased circulating blood, and fluid volume and cardiac output. Frequent monitoring of vital signs (initially monitored at least at hourly intervals) and urinary output is necessary for early detection of these complications. If bleeding goes undetected or is late in being detected, the patient may lose significant amounts of blood and may experience hypoxemia. In addition to hypovolemic shock due to hemorrhage, this type of blood loss may precipitate a myocardial infarction or transient ischemic attack. Bleeding may be suspected when the patient experiences fatigue and when urine output is less than 30 mL per hour. As bleeding persists, late signs of hypovolemia occur, such as cool skin, flat neck veins, and change in level of consciousness or responsiveness. Transfusions of blood components are indicated, along with surgical repair of the bleeding vessel. Pneumonia may be prevented through use of an incentive spirometer, adequate pain control, and early ambulation. Early signs of pneumonia include fever, increased heart and respiratory rates, and adventitious breath sounds. Preventing infection is the rationale for using asepsis when changing dressings and preparing catheters, other drainage tubes, central venous catheters, and intravenous catheters for administration of fluids. Insertion sites are monitored closely for signs and symptoms of inflammation: redness, drainage, heat, and pain. Special care must be taken to prevent urinary tract infection, which is associated with the use of indwelling urinary catheters. If antibiotic agents are prescribed, serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen levels must be monitored closely because many antibiotic agents are toxic to the kidney or can accumulate to toxic levels if renal function is decreased. Preventing fluid imbalance is critical when caring for a patient undergoing kidney surgery, because both fluid loss and fluid excess are possible adverse effects of the surgery. Fluid loss may occur during surgery as a result of excessive urinary drainage when the obstruction is removed, or it may occur if diuretic agents are used. Such loss may also occur with gastrointestinal losses, with diarrhea resulting from antibiotic use or with nasogastric drainage. When postoperative intravenous therapy is inadequate to match the output or fluids lost, a fluid deficit results. The proximal J hooks into the lower calix or renal pelvis, and the distal J curves into the bladder.

Psoriatic arthritis involving the sacroiliac and distal joints of the fingers may be overlooked antifungal essential oils list order 250 mg fulvicin overnight delivery, especially if the patient has the typical psoriatic lesions anti fungal infection fulvicin 250mg online. However fungus gnats house order fulvicin 250mg fast delivery, patients who complain of mild joint discomfort and some pitting of the fingernails may not be diagnosed with psoriasis until the more obvious cutaneous lesions appear anti fungal acne treatment proven fulvicin 250 mg. The complaint of joint discomfort in the patient with psoriasis should be noted and evaluated. Treatment of the condition usually involves joint rest, application of heat, and salicylates. The patient requires education about the care and treatment of the involved joints and the need for compliance with therapy. The incidence of psoriatic arthropathy is unknown because the symptoms are so variable. It is believed, however, that when the psoriasis is extensive and a family history of inflammatory arthritis is elicited, the chance that the patient will develop psoriatic arthritis increases substantially. It is recommended that a rheumatologist be consulted to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of the arthropathy. For example, the patient and the family caregiver may need to know that the topical agent anthralin leaves a brownish purple stain on the skin but that the discoloration subsides after anthralin treatment stops. The patient should also be instructed to cover lesions treated with anthralin with gauze, stockinette, or other soft coverings to avoid staining clothing, furniture, and bed linens. Patients using topical corticosteroid preparations repeatedly on the face and around the eyes should be aware that cataract development is possible. Strict guidelines for applying these medications should be emphasized because overuse can result in skin atrophy, striae, and medication resistance. If exposure is unavoidable, the skin must be protected with sunscreen and clothing. Gray- or green-tinted, wraparound sunglasses should be worn to protect the eyes during and after treatment, and ophthalmologic examinations should be performed on a regular basis. Nausea, which may be a problem in some patients, is lessened when methoxsalen is taken with food. Lubricants and bath oils may be used to help remove scales and prevent excessive dryness. No other creams or oils are to be used except on areas that have been shielded from ultraviolet light. The patient is kept under constant and careful supervision and is encouraged to recognize unusual changes in the skin. If indicated, referral may be made to a mental health professional who can help to ease emotional strain and give support. Belonging to a support group may also help patients acknowledge that they are not alone in experiencing life adjustments in response to a visible, chronic disease. The National Psoriasis Foundation publishes periodic bulletins and reports about new and relevant developments in this condition. Reports control of cutaneous lesions with no extension of disease Management of Patients With Dermatologic Problems 1681 Nursing Management Continual nursing assessment is carried out to detect infection. The disrupted, erythematous, moist skin is susceptible to infection and becomes colonized with pathogenic organisms, which produce more inflammation. Antibiotics, prescribed if infection is present, are selected on the basis of culture and sensitivity. It may be associated with chills, fever, prostration, severe toxicity, and an itchy scaling of the skin. There is a profound loss of stratum corneum (ie, outermost layer of the skin), which causes capillary leakage, hypoproteinemia, and negative nitrogen balance. Because of widespread dilation of cutaneous vessels, large amounts of body heat are lost, and exfoliative dermatitis has a marked effect on the entire body. It is considered to be a secondary or reactive process to an underlying skin or systemic disease. It may appear as a part of the lymphoma group of diseases and may precede the appearance of lymphoma. Preexisting skin disorders that have been implicated as a cause include psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis. It also appears as a severe reaction to many medications, including penicillin and phenylbutazone.
This pain can be caused by (1) a reduction in the size of the muscle compartment because the enclosing muscle fascia is too tight or a cast or dressing is constrictive anti yeast vegetarian diet fulvicin 250mg free shipping, or (2) an increase in muscle compartment contents because of edema or hemorrhage associated with a variety of problems (eg fungus gnats temperature order 250mg fulvicin free shipping, fractures fungus vegetable purchase 250mg fulvicin fast delivery, crush injuries) fungus gnats on cannabis plants 250 mg fulvicin with mastercard. The pressure within a muscle compartment may increase to such an extent as to decrease microcirculation, causing nerve and muscle anoxia and necrosis. Permanent function can be lost if the anoxic situation continues for longer than 6 hours. Assessment and Diagnostic Findings Frequent assessment of neurovascular function after fracture is essential. Paresthesia (burning or tingling sensation) and numbness along the involved nerve are early signs of nerve involvement. Motion is evaluated by asking the patient to move fingers or toes distal to the potential problem. Peripheral circulation is evaluated by assessing color, temperature, capillary refill time, swelling, and pulses. Pale or dusky and cold fingers or toes and prolonged capillary refill time suggest diminished arterial perfusion. Edema may obscure the presence of arterial pulsation, and Doppler ultrasonography may be used to verify a pulse. Pulselessness is a sign of arterial occlusion, not of compartment syndrome, because the tissue pressure would need to be above the systolic blood pressure for major artery occlusion to occur. As intracompartment pressure increases, the patient complains of deep, throbbing, unrelenting pain, which is greater than expected and not controlled by opioids. With continued nerve ischemia and edema, the patient experiences sensations of hypoesthesia (diminished sensitivity to stimulation) and then absence of feeling. The actual tissue pressure can be measured by inserting a tissue pressuremeasuring device into the muscle compartment. Prolonged pressure of more than 30 mm Hg can result in compromised microcirculation. Petechiae, possibly due to a transient thrombocytopenia, are noted in the buccal membranes and conjunctival sacs, on the hard palate, and over the chest and anterior axillary folds. Prevention and Management Immediate immobilization of fractures (including early surgical fixation), minimal fracture manipulation, adequate support for fractured bones during turning and positioning, and maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance are measures that may reduce the incidence of fat emboli. The nurse monitors high-risk patients (adults between 20 and 30 years of age with long bone, pelvic, or multiple fractures or crush injuries, and elderly patients with femur fractures) to identify this problem. The objectives of management are to support the respiratory system, to prevent respiratory and metabolic acidosis, and to correct homeostatic disturbances. Controlled-volume ventilation with positive end-expiratory pressure may be used to prevent or treat pulmonary edema. Corticosteroids may be administered to treat the inflammatory lung reaction and to control cerebral edema. Vasoactive medications to support cardiovascular function are administered to prevent hypotension, shock, and interstitial pulmonary edema. Accurate fluid intake and output records facilitate adequate fluid replacement therapy. Morphine may be prescribed for pain and anxiety for the patient who is on a ventilator. Because fat emboli are a major cause of death for patients with fractures, the nurse must recognize early indications of fat embolism syndrome and report them promptly to the physician. The physician needs to be notified immediately if neurovascular compromise is suspected. Compartment syndrome is managed by elevation of the extremity to the heart level, release of restrictive devices (dressings or cast), or both. If conservative measures do not restore tissue perfusion and relieve pain within 1 hour, a fasciotomy (surgical decompression with excision of the fibrous membrane that covers and separates muscles) may be needed to relieve the constrictive mus- Chapter 69 cle fascia. After fasciotomy, the wound is not sutured but instead is left open to permit the muscle tissues to expand; it is covered with moist, sterile saline dressings. Patients with fractures of the lower extremities and pelvis are at high risk for thromboembolism.

|
|